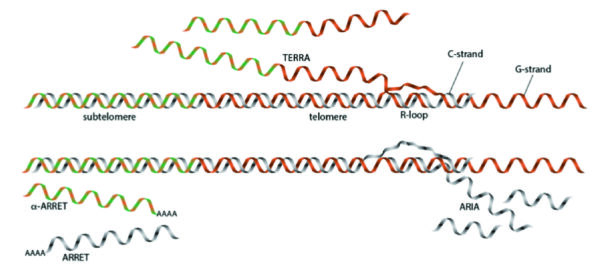
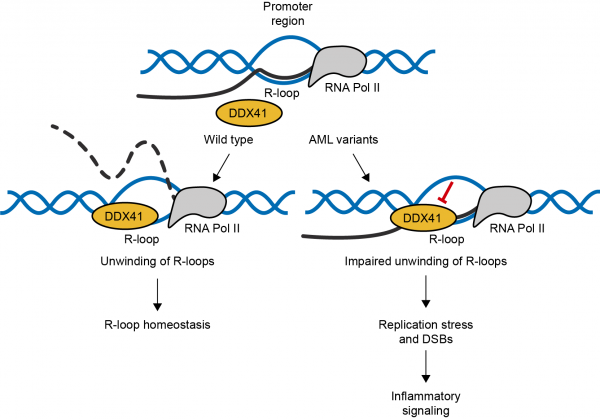
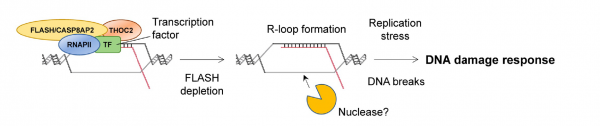
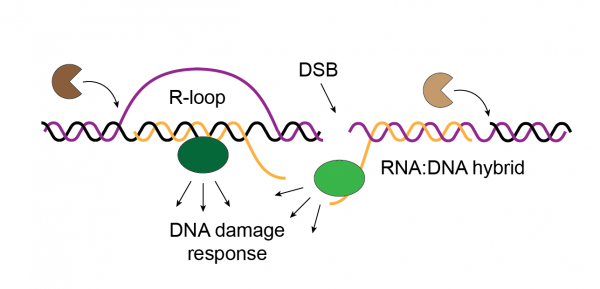
Project 1. R-loops modulating telomere maintenance and life span in fission yeast.
Telomeres are the nucleoprotein complexes that protect the ends of linear chromosomes from degradation and fusions. Telomeric DNA is transcribed into telomeric RNA (TERRA), which forms R-loops near chromosome ends. It has recently become clear that R-loops play a critical …
View MoreProject 2. Regulatory interplay between R-loops and transcription.
Transcription by RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) is essential to all cellular processes and hence to the adaptive response of cells to internal and external stimuli. The interplay between R-loops and transcription remains incompletely understood: R-loops have been reported to play …
View MoreProject 3. A role for FLASH/Casp8AP2 in R-loop regulation.
FLICE-associated huge protein (FLASH)/Caspase-8 associated protein 2 has been linked to various biological processes including death receptor-mediated signaling, transcriptional regulation via NF-kB and nuclear hormone receptors, Histone gene transcription, and Histone pre-mRNA processing of replication-dependent histone genes by interplay with …
View MoreProject 4. Understanding RNase H1 regulation at telomeres and beyond.
Telomere repeat-containing RNA (TERRA) R-loops (telR-loops) are formed at telomeres once per cell cycle and are removed prior to telomere replication. telR-loops likely have the function of preventing excessive DNA resection, which slows the rate of telomere shortening and prevents …
View MoreProject 5. Functional analysis of R-loops and RNA:DNA hybrids associated with DNA lesions.
R-loops play an ambiguous role in the genome: on the one hand, they are critical effectors of many cellular functions via their influence on gene expression. On the other hand, they pose a serious threat to genome integrity as they …
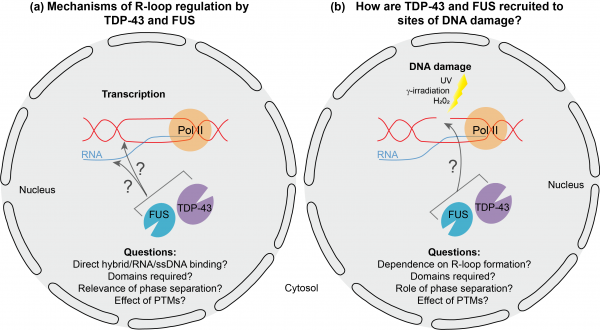
View MoreProject 6. R-loop regulation by neurodegeneration-linked DNA/RNA-binding proteins FUS and TDP-43.
R-loops occur naturally during transcription and can have important regulatory functions, however, persistence of R-loops can have deleterious effects and result in the accumulation of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and genome instability. Thus, aberrant R-loops have been linked to human …
View MoreProject 7. R-loop function in nuclear RNA interference.
Small RNA-guided gene regulatory pathways represent a widely conserved mode of control of gene expression and genome stability. In essence, these pathways use small RNA molecules to guide proteins of the Argonaute family to specific targets, which in eukaryotic organisms …
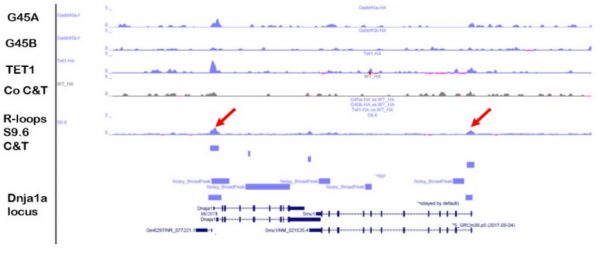
View MoreProject 8. Establishing protocols for genome-wide R-loop mapping.
R-loops are genomic DNA-RNA hybrids that are assembled either co-transcriptionally or by local unwinding of DNA and hybridization of homologous RNA fragments. A subclass, regulatory R-loops, is involved in epigenetic gene regulation. We previously described the stress response protein Gadd45a …
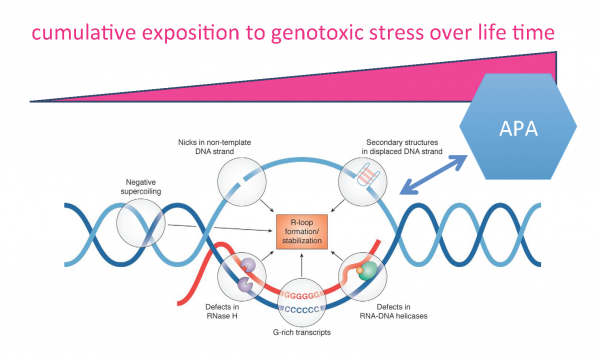
View MoreProject 9. Crosstalk between R-loop formation and alternative polyadenylation.
Alternative polyadenylation (APA) is a widespread and highly dynamic mechanism of gene regulation. It affects more than 70% of all genes, resulting in transcript isoforms with distinct 3’end termini. APA thereby considerably expands the diversity of the transcriptome 3′ end, …
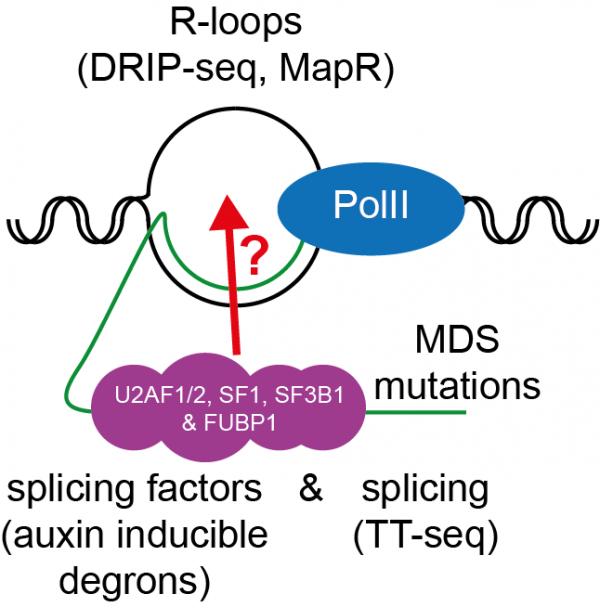
View MoreProject 10. Gene paralogues, RNA processing and R-loops.
RNA splicing alterations lead to R-loop accumulation, inducing replication stress and chromosome fragility, potentially contributing to pathological states, such as neurodegeneration. Despite intricate RNA processing across higher eukaryotic organs, knowledge about cell-specific R-loop roles during cellular differentiation is limited. Our …
View MoreProject 11. The interplay between RNA splicing and R-loop formation.
The project was terminated because Dr. Julian König received a professorship at the University of Würzburg, and re-allocated his lab. Alternative splicing is crucial for generating transcriptome and proteome diversity during development and for fostering tissue identity. As a …
View MoreProject 12. Regulation of alternative splicing by R-loop formation in plants.
Alternative precursor mRNA splicing (AS) generates transcript isoforms that can have distinct functions and represents a major means to diversify gene expression in higher eukaryotes. The mechanisms underlying AS regulation are versatile and, in many cases, the regulatory principles are …
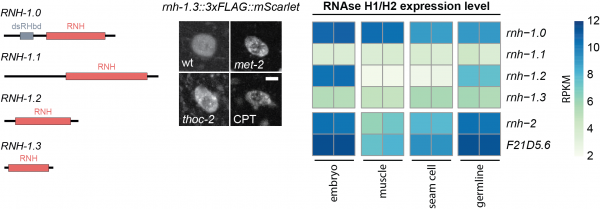
View MoreProject 13. Regulation and specificity of RNase H1 enzymes.
An R-loop is an RNA-DNA hybrid that displaces the second DNA strand. R-loops occur frequently in genomes and have significant physiological importance, regulating gene expression and telomere stability. On the other hand, R-loops are a source of genomic instability e. …
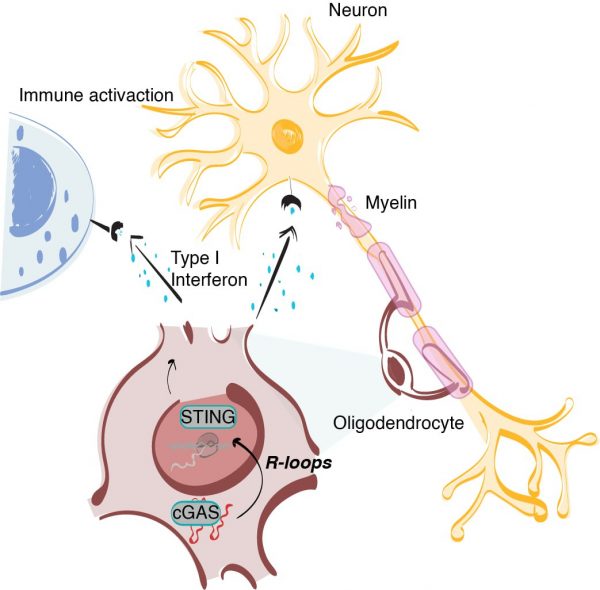
View MoreProject 14. Regulation and function of R-loops in auto-immunity and sex-bias.
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease characterized by the immune system’s misguided attack on myelinating neurons, with an onset appearance around midlife, which causes a progressive disruption of the normal central nervous system function. Over the past few years, its …
View MoreProject 15. Investigating the life cycle of RAD51AP1-mediated R-loops.
Telomeres, initially thought to be transcriptionally inactive, are transcribed and produce non-coding RNA known as TERRA (telomeric repeat-containing RNA). TERRA RNA can hybridize with telomeric DNA to form telomeric R-loops (tR-loops). These tR-loops are elevated in ALT-positive cancers and have …
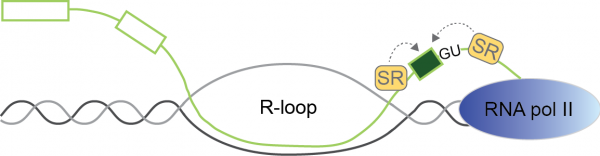
View MoreProject 16. Understanding the influence of eRNA association modes on transcriptional condensates.
Multicellular organisms rely on differential gene expression to create cellular diversity. Precise gene regulation is crucial, as failures can lead to reduced fitness, developmental defects, and disease. Enhancers, DNA elements with binding sites for transcription factors, play a key role …
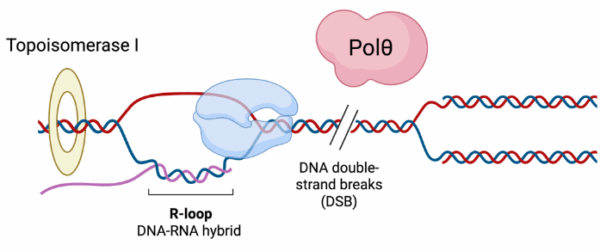
View MoreProject 17. DNA polymerase Theta (POLΘ) on mediating R-Loop-induced genome instability.
R-loops are three-stranded nucleic acid structures consisting of an RNA-DNA hybrid and a displaced single-stranded DNA1. They form naturally during transcription, where they regulate gene expression, chromatin structure, and DNA repair processes such as immunoglobulin class-switch recombination (CSR) and telomere …
View More